Thai Airways International Overview
Thai Airways International Public Company Limited, commonly known as Thai Airways, is the flag carrier airline of Thailand. Here is an overview of Thai Airways International:
Table of Contents
Founding and History:
- Thai Airways was founded on March 29, 1960, and began operations on May 1, 1960. The airline was established as a joint venture between Thailand’s domestic carrier, Thai Airways Company (TAC), and Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS).
Ownership:
- Thai Airways is majority-owned by the Thai government through the Ministry of Finance. The government holds a significant stake in the airline.
Hub and Bases:
- Suvarnabhumi Airport (BKK) in Bangkok serves as the main hub for Thai Airways. The airline also has secondary hubs at Phuket International Airport (HKT) and Chiang Mai International Airport (CNX).
Fleet:
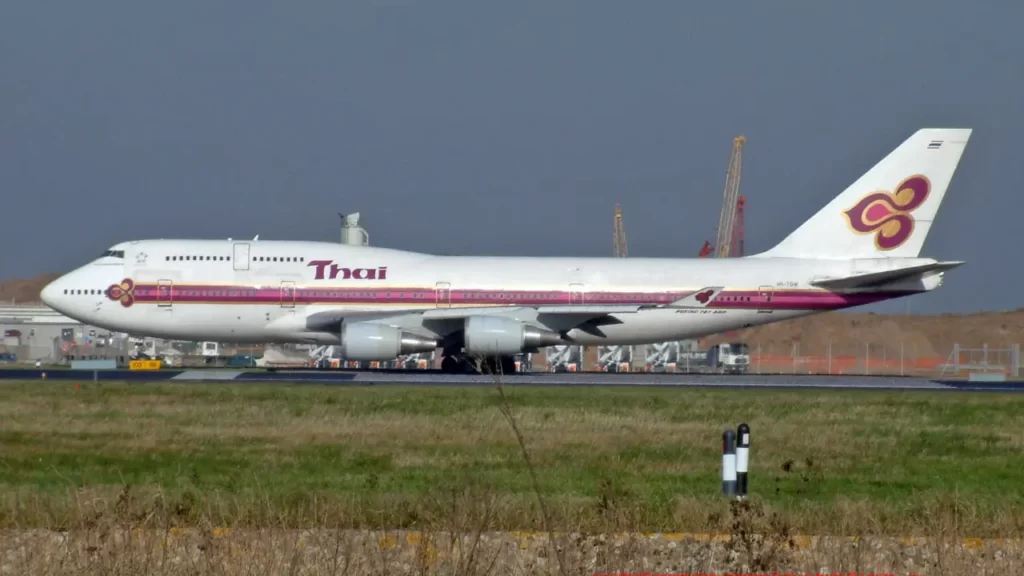
- Thai Airways operates a diverse fleet that includes a mix of Airbus and Boeing aircraft. The fleet includes various models such as the Airbus A350, Boeing 777, and Boeing 787 Dreamliner.
Star Alliance Membership:
- Thai Airways is a member of the Star Alliance, one of the world’s largest global airline alliances. This membership allows for cooperation and codeshare agreements with other member airlines.
Services and Classes:
- Thai Airways offers a range of services, including multiple cabin classes. These typically include Royal First Class, Royal Silk Class (Business Class), and Economy Class. Passengers in premium classes enjoy enhanced amenities and services.
In-Flight Entertainment and Amenities:
- Thai Airways provides in-flight entertainment, including movies, music, and games, on its long-haul flights. Premium class passengers have access to additional amenities, such as lie-flat seats, priority check-in, and lounge access.
Royal Orchid Plus Frequent Flyer Program:
- Thai Airways operates a frequent flyer program called Royal Orchid Plus. Passengers can earn miles for their flights and redeem them for various benefits, including award tickets and upgrades.
Environmental Initiatives:
- Like many airlines, Thai Airways has implemented measures to improve fuel efficiency and reduce its environmental impact. This includes the introduction of more fuel-efficient aircraft into its fleet.
Financial Challenges and Restructuring:
- Thai Airways has faced financial challenges, including increased competition and the impact of events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. The airline has undergone restructuring efforts to address financial issues.
Impact of COVID-19:
- The COVID-19 pandemic significantly affected the global aviation industry, including Thai Airways. The airline implemented measures to adapt to reduced demand, including schedule adjustments and cost-cutting initiatives.
Thai Airways International History

Thai Airways International Public Company Limited, commonly known as Thai Airways, has a history that spans several decades. Here is an overview of key milestones in the history of Thai Airways:
Founding and Inaugural Flight (1960):
- Thai Airways was founded on March 29, 1960, as a joint venture between Thailand’s domestic carrier, Thai Airways Company (TAC), and Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS).
- The airline officially began operations on May 1, 1960, with its inaugural flight from Bangkok to Kuala Lumpur.
Early Expansion and Fleet Growth:
- In the early years, Thai Airways expanded its network regionally and internationally, connecting Bangkok with major cities in Asia and beyond.
- The airline added various aircraft to its fleet, including turboprop and jet aircraft, to support its growing operations.
Transition to Jet Age (1970s):
- Thai Airways transitioned to the jet age with the introduction of jetliners, including the Boeing 707 and later the Boeing 747. This facilitated the airline’s expansion into long-haul routes.
Continued Growth and Fleet Modernization (1980s-1990s):
- Thai Airways experienced significant growth during the 1980s and 1990s, adding more destinations and expanding its fleet with modern wide-body aircraft.
- The airline introduced the Boeing 777 and Airbus A300 as part of its fleet modernization efforts.
Star Alliance Membership (1997):
- Thai Airways became a member of the Star Alliance, one of the largest global airline alliances, in 1997. This membership allowed for increased cooperation and codeshare agreements with other member airlines.
Privatization (1991-2003):
- Thai Airways underwent a privatization process during the early 1990s, with the Thai government reducing its stake in the airline. The process aimed to enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
Expansion into Low-Cost Market (2004):
- Thai Airways entered the low-cost market with the establishment of Thai Smile Airways in 2012. Thai Smile operated as a subsidiary, focusing on regional and domestic routes.
Financial Challenges and Restructuring (2010s):
- In the 2010s, Thai Airways faced financial challenges, including increased competition, political instability, and the impact of events such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The airline initiated restructuring efforts to address financial issues and improve its operational efficiency.
Suspension of Operations and Rehabilitation (2020):
- In 2020, facing severe financial difficulties exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, Thai Airways suspended its operations. The Thai government announced plans for the airline to undergo a court-sanctioned rehabilitation process.
Ongoing Rehabilitation (2021 Onward):
Thai Airways continues its rehabilitation process, which involves addressing financial liabilities, restructuring debts, and developing a sustainable business plan for the future.
Thai Airways has played a vital role in connecting Thailand with the rest of the world and has been a symbol of the country’s aviation industry. The ongoing rehabilitation process will shape the airline’s future and its role in the global aviation landscape. For the latest and most accurate information about Thai Airways, including its current status and recent changes, it is recommended to check the official Thai Airways website and recent news sources.